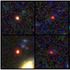
Six massive ancient galaxies that astronomers are calling “cosmic busters” appear to have been discovered, which could upend existing cosmological theories.
Galaxy discovered at £8.3bn cost james webb telescopebelieved to date back to within about 600 million years of the Big Bang.
While the 100-year-old telescope has discovered much older galaxies dating back within 300 million years of the universe’s beginning, the size and maturity of the giant galaxies has astounded scientists.
When astronomers spotted these “monsters,” they thought they had made a mistake.
Lead researcher Ivo Labbe, from Australia’s Swinburne University of Technology, said: “While most galaxies of this era are still small and will only grow larger over time, there are some samples that mature rapidly. Why this is so, Or how this will work is unclear.”
“We’re in shock, a little bit in disbelief,” Mr Rabe said.
The six galaxies appear to be billions of times the mass of the sun, according to scientists who published their findings in the journal Nature.
But they are believed to be very compact, packing as many stars as the Milky Way, but in a relatively small space.
Joel Leja of Penn State University, who worked on the study, said the finding “upends what many of us think of as solid science.”
read more:
NASA’s James Webb Space Telescope finds signs of ‘building blocks of life’ in icy clouds
“It turns out that we found something so unexpected that it actually raises questions for science. It calls into question the whole picture of early galaxy formation.”
Existing theories suggest that after a period of rapid expansion, the universe took hundreds of millions of years to cool enough for gas to coalesce and collapse into the first stars, and galaxies began to form. This period is known as the Dark Ages.
The observations of the new galaxy come from a dataset from the Webb Telescope.
nasa The European Space Agency’s Webb Telescope is considered the successor to the Hubble Space Telescope, which was launched nearly 33 years ago.
Unlike Hubble, the larger and more powerful Webb telescope can see through dust clouds with infrared vision to find previously undiscovered galaxies.
Scientists hope to eventually observe the first galaxies and stars that formed after the universe formed 13.8 billion years ago.
The team is still awaiting official confirmation of the galaxy through sensitive spectroscopy. Some of the objects may not be galaxies, but obscuring supermassive black holes, Mr Leja said.
While some may become smaller, there is a good chance that “at least some of them will end up” as galactic giants, Mr Labbe said. “Next year will tell us.”